Events

Fatty Liver Disease is a growing concern worldwide as well as in Singapore. It is known as the “Silent Killer” and can silently progress towards more serious conditions such as cirrhosis (scarring) and liver cancer. Liver cancer is the 5th most common cancer among males in Singapore. Although liver cancer is less common in females, it is still the third highest cause of deaths in both genders and this is because only 20% of primary liver cancers are diagnosed at an early stage. With early detection and prevention, fatty liver disease can be managed and liver cancer can be prevented.
Registration for our Better Liver, Better Health Screening Campaign is now closed. Thank you to everyone who registered!
Check out our other ongoing free cancer screening campaigns!
About Fatty Liver
Fatty liver disease is a common chronic liver disease where excess fat is deposited in the liver of people who drink little or no alcohol and can lead to liver cirrhosis (scarring) and liver cancer. The good news is, fatty liver disease can be reversible with the right lifestyle approach. However, if it is not managed properly, fatty liver disease can lead to more serious conditions such as cirrhosis (scarring) and liver cancer.
Steps to reverse a fatty liver:
- Weight loss
- Improve diet
- Regular exercise
Signs and Symptoms
Individuals with early fatty liver disease usually shows no symptoms. However, if symptoms are present, it may be non-specific symptoms that includes:
- Tiredness
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in the right upper abdomen
Causes and Risk Factors
- Family History/Hypertension/Hyperlipidemia (High Cholesterol)
- Obesity
- Hepatitis B Carrier
- Hepatitis C Carrier
- Metabolic Conditions/Diabetic patients
How to Prevent Fatty Liver Disease
- Healthy weight loss
- Well-balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Control of diabetes, hypertension, obesity, cholesterol
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
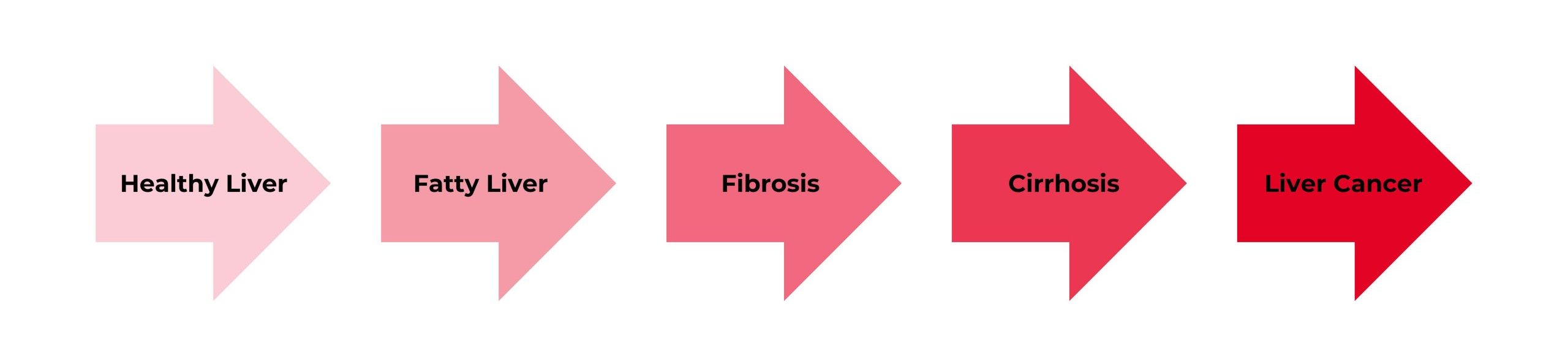
How is Liver Disease Linked to Liver Cancer?
Only 20% of primary liver cancers, Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) are diagnosed at an early stage. HCC develops in patients with chronic liver disease. Around 80-90% of HCC was developed in cirrhotic livers and 15% of HCC was developed without prior cirrhosis. There are various causes of HCC in Southeast Asia:
- 31% of HCC is due to Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD)
- 26% of HCC is due to Hepatitis B infection
- 22% of HCC is due to Hepatitis C infection
- 21% of HCC is due to other causes e.g., Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), aflatoxin